The Fisher Center for Business Analytics coordinates a range of educational programs that applies UC Berkeley’s leadership in Data Science to business and reflects the distinct brand of the Berkeley Haas Defining Leadership Principles:
Integrated

The Haas School of Business develops leaders. At Haas, courses introduce principles of data analytics in the context of business and leadership. Business analytics is framed not as a distinct subject but as fundamental to every discipline. The curriculum is coordinated to enable a student to learn basic concepts (e.g. supervised v. unsupervised learning, evaluating the performance of a categorical classifier, experimental design) through one of several different courses. Analytics is thus diffused throughout the general, MBA curriculum.
Curriculum
The Haas analytics curriculum is deliberately coordinated in a layered fashion. All students are required to take Data and Decisions so as to achieve basic literacy in quantitative analysis. Students interested in understanding the landscape of business analytics concepts may select from one or more Primary Analytics courses. The syllabi of the Primary courses are coordinated to maximize complementarities (and minimize redundancies) among methods and problem-domains while providing the next level of depth in quantitative, data-driven decision-making. Beyond the Primary courses are a number of Secondary, domain-specific courses. Each includes additional quantitative, analytics modules.
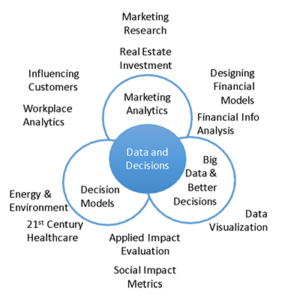
The Haas School is part of the broader UC Berkeley community. Students at Haas may weave threads from programs across the University into their studies. UC Berkeley’s programs in Statistics, Computer Science, Mathematics, and Information are defining the leading edge of Data Science. Haas students have the opportunity to pursue advanced studies from global experts across the University.
Technology Platform
In addition to Excel, Haas has deployed a common technology platform for business analytics. The Jupyter Notebook is a technology standard in the data science community. Although open source, Jupyter was largely invented and currently developed and maintained at UC Berkeley. Jupyter is one implementation of the Notebook paradigm. R-studio, a popular interface for R now has a format that mimics the notebook paradigm as does Matlab (these are other software tools for algorithmic data manipulation). Haas supports the Jupyter environment through a software-as-a- service platform called JupyterHub which students access via a Web browser. Depending upon the course, students use use R or Python. No one tool strictly dominates the other; they stem from different traditions. Python is more common in the engineering-based courses. R is more common in advanced statistics courses. At UC Berkeley, both the Statistics and EECS (Electrical Engineering and Computer Science) departments have converged on Python as the base platform for all introductory courses and teach using Jupyter notebooks.

The Graduate Certificate in Business Analytics responds to an escalating need for leaders and managers who can translate data into business insights and who are literate consumers of data science techniques. It is designed for students aspiring to leadership roles involving business decision making informed by data.

Executive and Professional Education
Executive and Professional Education Programs in Business Analytics bring business leaders to campus to continue their lifelong education. Courses in analytics include open-enrollment programs as well as opportunities for custom programs through Berkeley’s Center for Executive Education.
The program helps coordinate three regional networks of strategic information technology leaders who meet monthly to educate and support one another (Silicon Valley, San Francisco, East Bay).
With the Gartner Group, the Center established the Fisher-Hopper Prize for Lifetime Achievement in CIO Leadership.
Each year, the prize ceremony is part of an annual, day-long seminar on strategic information technology
Doctoral

Through the support of the Ryoichi Sasakawa Foundation, the Center administers Fellowships to PhD students applying analytics in their doctoral research. Current Fellows in Business Analytics are:















